/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/45583662/shutterstock_61564156.0.0.jpg)
Introduction to LANs, WANs, and Other Kinds of Area Networks

Common types of area networks are:
1. LAN - Local Area Network
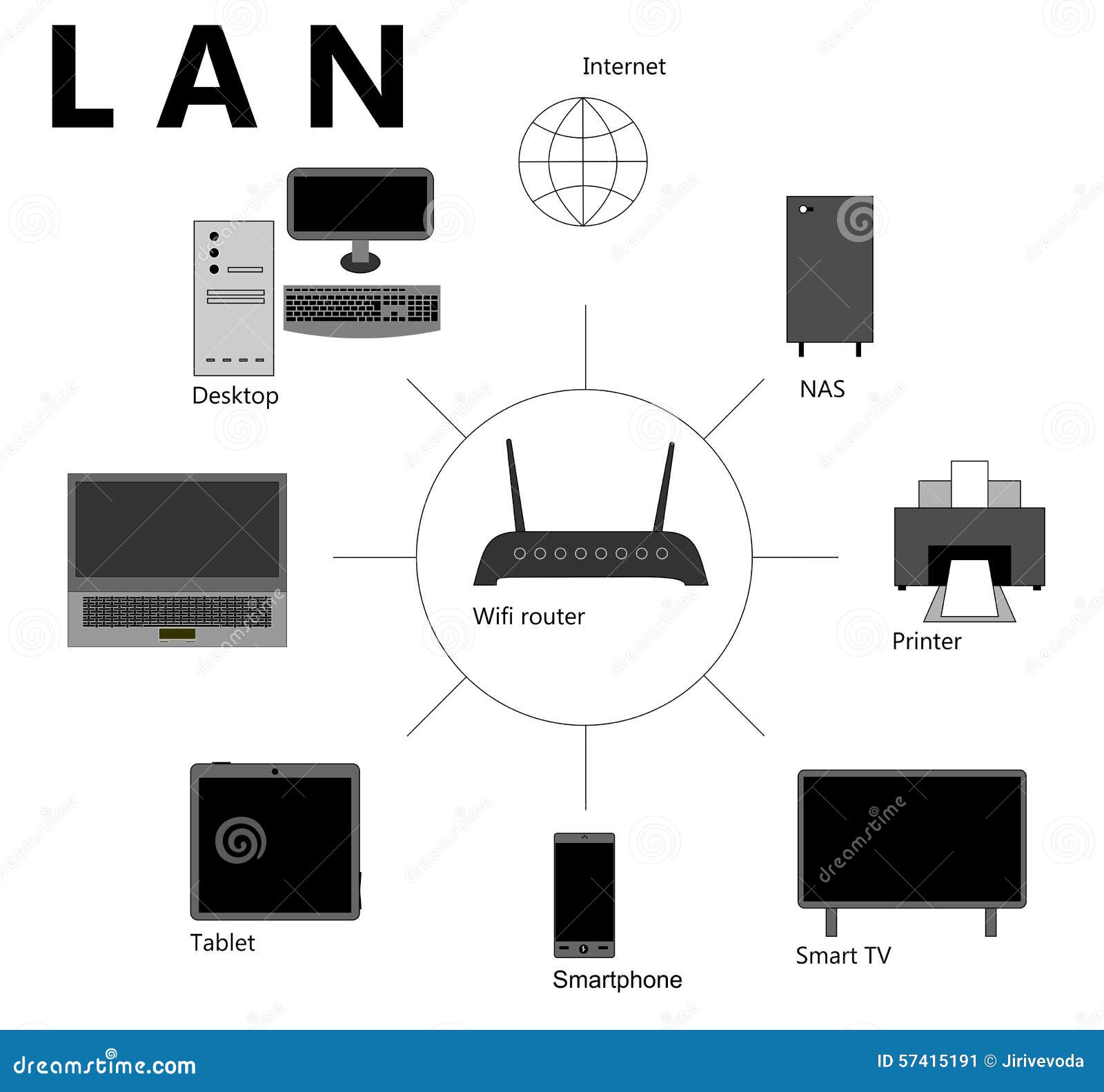
LAN (LOCAL AREA NETWORK)
A LAN connects network devices over a relatively short distance. A networked office building, school, or home usually contains a single LAN, though sometimes one building will contain a few small LANs (perhaps one per room), and occasionally a LAN will span a group of nearby buildings. In TCP/IP networking, a LAN is often but not always implemented as a single IP subnet.
LANs are typically used for single sites where people need to share resources among themselves but not with the rest of the outside world. Think of an office building where everybody should be able to access files on a central server or be able to print a document to one or more central printers. Those tasks should be easy for everybody working in the same office, but you would not want somebody just walking outside to be able to send a document to the printer from their cell phone! If a local area network, or LAN, is entirely wireless, it is referred to as a wireless local area network or WLAN.
2. PAN - Personal Area Network

PAN (PERSONAL AREA NETWORK)
A personal area network, or PAN, is a computer network organized around an individual person within a single building. This could be inside a small office or residence. A typical PAN would include one or more computers, telephones, peripheral devices, video game consoles and other personal entertainment devices.
This type of network provides great flexibility. For example, it allows you to:
- Send a document to the printer in the office upstairs while you are sitting on the couch with your laptop.
- Upload a photo from your cell phone to your desktop computer.
- Watch movies from an online streaming service to your TV.
3. MAN - Metropolitan Area Network

MAN (METROPOLITAN AREA NETWORK)
A metropolitan area network, or MAN, consists of a computer network across an entire city, college campus or small region. A MAN is larger than a LAN, which is typically limited to a single building or site. Depending on the configuration, this type of network can cover an area from several miles to tens of miles. A MAN is often used to connect several LANs together to form a bigger network. When this type of network is specifically designed for a college campus, it is sometimes referred to as a campus area network, or CAN.
4. WAN - Wide Area Network

A wide area network, or WAN, occupies a very large area, such as an entire country or the entire world. A WAN can contain multiple smaller networks, such as LANs or MANs. The Internet is the best-known example of a public WAN.
Sources:
https://study.com/academy/lesson/types-of-networks-lan-wan-wlan-man-san-pan-epn-vpn.html
https://www.lifewire.com/lans-wans-and-other-area-networks-817376
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/5079/personal-area-network-pan